Understanding Anxiety: Strategies for Managing Stress and Overcoming Challenges
April 13, 2024
Aging Gracefully: Top Nutritional Tips for Maintaining Vitality After 60
May 24, 2024The intricate connection between the gut and the brain has long fascinated researchers and health enthusiasts alike. While traditionally viewed as separate entities, emerging scientific evidence suggests that the gut and the brain are closely interconnected, forming what is often referred to as the “gut-brain axis.” This bidirectional communication system plays a crucial role in various aspects of health, including digestion, immunity, and surprisingly, mood regulation. In this article, we’ll explore the fascinating relationship between digestive health and mood and how nurturing your gut can positively impact your mental well-being.
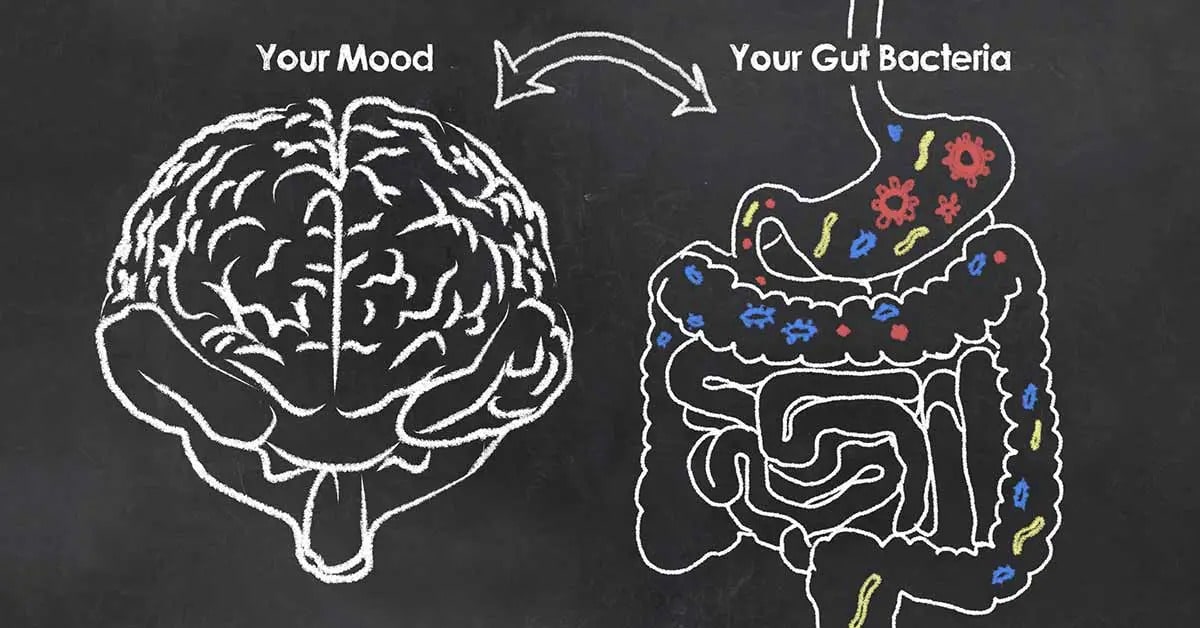
Understanding the Gut-Brain Axis
The gut-brain axis is a complex network of communication pathways that allows constant communication between the gastrointestinal tract and the central nervous system. This communication occurs through various channels, including the nervous system, immune system, and hormonal signaling. The gut is home to trillions of microorganisms collectively known as the gut microbiota, which play a key role in regulating gut health and influencing brain function.
The Role of the Gut Microbiota
The gut microbiota, consisting primarily of bacteria but also including viruses, fungi, and other microorganisms, plays a crucial role in maintaining gut health and overall well-being. These microorganisms help digest food, produce essential nutrients, regulate immune function, and protect against harmful pathogens. Moreover, emerging research suggests that the gut microbiota can influence brain function and behavior through the production of neurotransmitters, metabolites, and other signaling molecules.
Impact on Mood and Mental Health
The influence of the gut microbiota on mental health and mood regulation is a rapidly growing area of research. Studies have found associations between alterations in gut microbiota composition and various mental health conditions, including depression, anxiety, and stress-related disorders. Additionally, animal studies have demonstrated that manipulating the gut microbiota through probiotics, prebiotics, or fecal transplants can have profound effects on behavior, mood, and stress responses.
How Digestive Health Affects Mood
Several mechanisms have been proposed to explain how digestive health affects mood and mental well-being:
- Neurotransmitter Production: The gut microbiota can produce neurotransmitters such as serotonin, dopamine, and gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), which play key roles in mood regulation. Imbalances in these neurotransmitters have been linked to mood disorders such as depression and anxiety.
- Inflammation: Disruptions in gut health can lead to increased intestinal permeability (leaky gut) and chronic low-grade inflammation, which have been implicated in the development of mood disorders. Inflammatory cytokines can affect neurotransmitter function and contribute to symptoms of depression and anxiety.
- Hormonal Signaling: The gut microbiota can influence the production and signaling of hormones such as cortisol and insulin, which play roles in stress responses and mood regulation. Dysregulation of these hormonal pathways can contribute to mood disturbances and mental health disorders.
Nurturing Your Gut for Better Mood
Given the strong link between digestive health and mood, taking care of your gut is essential for promoting mental well-being. Here are some tips to nurture your gut and support a healthy mood:
- Eat a Balanced Diet: Consume a diverse range of fiber-rich fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and fermented foods to nourish your gut microbiota and promote digestive health.
- Limit Processed Foods: Minimize intake of processed foods, refined sugars, and artificial additives, which can disrupt gut microbiota balance and contribute to inflammation.
- Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of water throughout the day to support digestion, nutrient absorption, and the elimination of waste products from the body.
- Manage Stress: Practice stress-reducing techniques such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, yoga, or mindfulness to reduce stress levels and support gut-brain axis function.
- Get Adequate Sleep: Prioritize quality sleep to allow your body to rest, repair, and rejuvenate, which is essential for both gut health and mental well-being.
- Consider Probiotics: Incorporate probiotic-rich foods such as yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, and kimchi into your diet to introduce beneficial bacteria to your gut microbiota.
- Seek Professional Help: If you’re experiencing persistent mood disturbances or mental health symptoms, don’t hesitate to seek help from a qualified healthcare professional for evaluation and treatment.
The gut-brain connection highlights the intricate interplay between digestive health and mood regulation. By nurturing your gut through healthy lifestyle habits, you can support optimal gut microbiota balance and promote mental well-being. By prioritizing digestive health, you can take proactive steps to enhance your mood, reduce stress, and cultivate a greater sense of overall happiness and vitality.