Ten Benefits of a Colonoscopy
September 24, 2024
Essential Health Screenings After 50: What You Need to Know
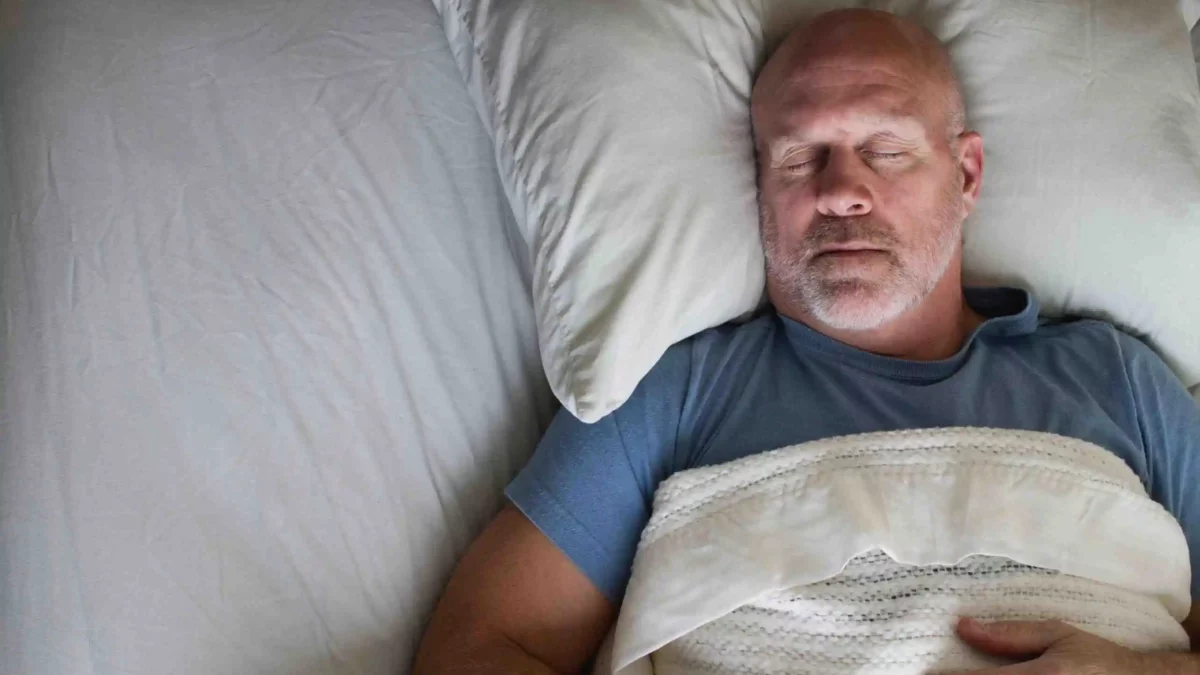
November 24, 2024As we age, sleep patterns often change and can become a source of frustration and concern. Many seniors find themselves waking up earlier, sleeping less deeply, or experiencing frequent interruptions throughout the night. Good sleep, however, is crucial for physical health, emotional balance, and overall quality of life. This comprehensive blog post will explore practical strategies for improving sleep among seniors, helping them achieve the restful nights they need.
Understanding Sleep Challenges in Seniors
Several factors contribute to changes in sleep patterns among older adults. These can include health conditions like sleep apnea, restless leg syndrome, and the side effects of medications. Psychological factors such as stress or depression can also disrupt sleep, as can environmental disturbances like noise, light, or an uncomfortable bedroom. Understanding these challenges is the first step toward finding solutions that promote better sleep.
Tips for Improving Sleep After 65
1. Establish a Consistent Sleep Schedule:
Going to bed and waking up at the same time every day can significantly improve the quality of your sleep. Consistency reinforces your body’s sleep-wake cycle, making it easier to fall asleep and wake up naturally.
2. Optimize Your Sleep Environment:
Create a room that is conducive to sleeping. This means cool, comfortable, and free from any noise that could disturb your sleep. Consider using blackout curtains, eye masks, earplugs, and “white noise” machines. Ensure your mattress and pillows are supportive and comfortable.
3. Limit Nap Times:
While napping can be a good way to catch up on missed sleep, long or frequent naps during the day can adversely affect your nighttime sleep. If you choose to nap, limit yourself to about 20-30 minutes and avoid doing so late in the day.
4. Be Mindful of What You Eat and Drink:
Your eating habits play a role in how well you sleep, especially in the hours before bedtime. Be cautious with nicotine, caffeine, and alcohol, as these can disrupt sleep. Also, avoid heavy or large meals within a couple of hours of bedtime. If you’re hungry at night, eat a light, healthy snack.
5. Engage in Regular Physical Activity:
Regular physical activity can help you fall asleep faster, enjoy deeper sleep, and wake feeling more energetic and refreshed. However, timing is crucial—exercise too close to bedtime can be stimulating. Try to schedule exercise at least three hours before bed.
6. Manage Worries:
Try to resolve your worries or concerns before bedtime. Jot down what’s on your mind and then set it aside for tomorrow. Stress management might help. Techniques such as meditation, deep breathing, and relaxation exercises can be done before bedtime to help calm your mind.
7. Establish a Pre-Sleep Routine:
Develop a ritual that tells your body it’s time to wind down. This can include reading a book, listening to soothing music, or taking a warm bath. It’s helpful to do these activities away from bright lights and stimulating activities, such as TV or computer screens.
8. Use Light to Your Advantage:
Natural light keeps your circadian rhythms in check. Expose yourself to sunlight in the morning and avoid bright lights in the evening, especially blue light from screens, as it can impact your ability to fall asleep.
9. Review Your Medications:
Sometimes, medications can interfere with sleep. If you suspect that a medication is affecting your sleep, talk to your doctor about adjusting the dosage or changing medications.
10. Consider Professional Help:
If you’ve tried multiple strategies and your sleep problems continue, it may be time to consult a healthcare provider. They can help you determine the cause of your sleep issues and recommend appropriate treatments, which may include behavioral therapy or sleep studies.
Sleep and Health Connection
Quality sleep is more than just a matter of feeling rested. Sleep affects various aspects of your health:
- Immune Function: Adequate sleep helps to fight off infections.
- Mental Health: Sleep affects your mood and can decrease the risk of depression and anxiety.
- Cognitive Function: Good sleep supports brain function and is important for memory and learning.
- Physical Health: Sleep is crucial for repairing the heart and blood vessels and balancing hormones that manage appetite, growth, and stress.
Achieving restful nights is essential for your health and well-being, especially as you age. By implementing practical steps to improve sleep habits and environments, seniors can enhance their quality of sleep and, by extension, their quality of life. Regular sleep schedules, optimized sleep environments, physical activity, and managing dietary and psychological factors can all contribute to better sleep. Remember, it’s important to consult healthcare providers for persistent sleep issues to ensure any underlying conditions are appropriately managed. With the right strategies, restful and rejuvenating sleep can be within reach, helping you to remain healthy, energetic, and vibrant in your senior years.

